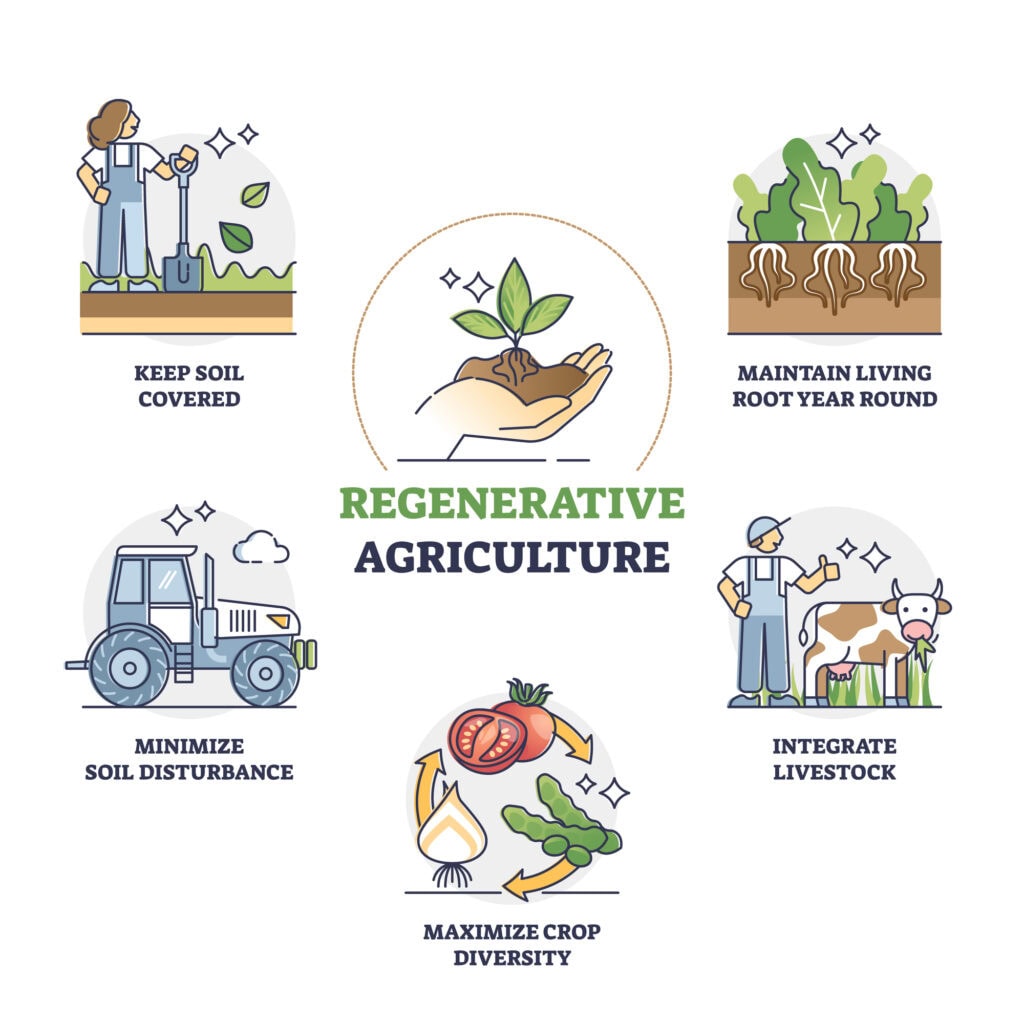
Regenerative agriculture is changing the way farming is done, bringing the focus back to soil health, biodiversity, and sustainability. One of the key components driving this revolution is the use of beneficial bacteria. These naturally occurring microorganisms are essential to improving soil quality, enhancing crop yields, and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. Let’s dive into how regenerative agriculture, powered by beneficial bacteria, is transforming modern farming.
The Role of Beneficial Bacteria in Regenerative Agriculture
Beneficial bacteria are microscopic organisms that live in the soil and play a critical role in nutrient cycling. They break down organic matter, converting it into essential nutrients that plants can absorb. In regenerative agriculture, these bacteria are harnessed to improve soil fertility naturally, reducing the need for chemical inputs that can harm the environment.
One of the most important ways beneficial bacteria contribute to regenerative farming is by promoting soil structure. Healthy soil with a rich microbial community holds water better, improves aeration, and creates an environment where plants can thrive. This results in stronger, more resilient crops that are better able to withstand pests, diseases, and drought.
Why Regenerative Agriculture is Gaining Popularity
Regenerative agriculture, with its emphasis on natural processes, is becoming increasingly popular as farmers look for sustainable alternatives to conventional farming practices. The use of beneficial bacteria aligns perfectly with this movement because it focuses on restoring the natural balance of the soil. Instead of depleting the soil with chemicals, regenerative farming enriches it, leading to long-term benefits for both the land and the crops.
Another reason for the growing interest in regenerative practices is the environmental impact. Traditional farming often leads to soil degradation, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. Regenerative agriculture, however, helps reverse these negative effects by rebuilding the soil’s microbial ecosystem, promoting carbon sequestration, and increasing biodiversity on farms.
How Beneficial Bacteria Improve Crop Yields
The presence of beneficial bacteria in the soil leads to healthier plants, which in turn produce higher yields. These bacteria help plants absorb nutrients more efficiently, allowing them to grow faster and stronger. In regenerative agriculture, the use of biofertilizers—natural products that contain beneficial bacteria—further boosts crop growth by reducing the dependence on synthetic fertilizers.
Farmers using regenerative methods report improved soil health year after year, which leads to increased yields without the need for heavy chemical inputs. This creates a more sustainable farming system that benefits both the environment and the economy.
As regenerative agriculture continues to gain momentum, the role of beneficial bacteria will remain at the forefront of this agricultural revolution. By embracing these natural processes, farmers are not only protecting the environment but also ensuring the long-term success of their crops and their livelihoods.
Ready to harness the power of regenerative agriculture? By incorporating beneficial bacteria into your farming practices, you can improve soil health, increase crop yields, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
References:
- Soil Science Society of America. The Importance of Beneficial Bacteria in Soil Health.
- Regenerative Agriculture Initiative. The Role of Microbial Communities in Sustainable Farming.
- Journal of Sustainable Agriculture. How Regenerative Practices are Redefining Modern Farming.